Can Depression Cause Memory Loss?
Depression isn't just about feeling down; it can also impact cognitive functions, including memory. Many people experiencing depression notice changes in their ability to remember things. This blog explores how depression can affect memory and what you can do about it.
How Depression Affects Memory
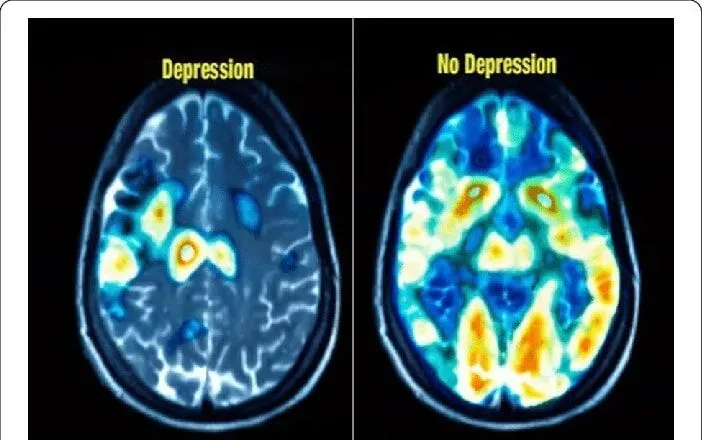
Depression primarily influences mood and emotions but also significantly impacts memory. The brain's hippocampus, crucial for forming and retrieving memories, can shrink in response to chronic depression. This reduction in size affects how memories are stored and recalled.
- Negative Bias: Depression often skews memory recall towards negative events. This bias makes it difficult for individuals to remember positive experiences, further exacerbating feelings of hopelessness.
- Neurogenesis Suppression: Chronic stress from depression can suppress neurogenesis, the process of creating new neurons in the hippocampus. This impairment leads to difficulty in forming new memories and can hinder the ability to learn and remember new information.
- Short-Term Memory Issues: People with depression often struggle with short-term memory. Forgetfulness about daily tasks or recent events is common and can make everyday functioning more challenging.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Depression can lead to trouble focusing and concentrating, which can affect memory retention. Distraction and a lack of mental clarity make it harder to encode and retrieve information effectively.
The Role of Stress in Memory Problems
Stress, a common companion to depression, plays a significant role in memory issues. Elevated cortisol levels, caused by prolonged stress, can interfere with the brain’s ability to store and recall information. This stress response can further impair memory function, creating a cycle of cognitive difficulties.
Long-Term Effects on Memory
Long-term depression can lead to persistent memory problems. As the condition continues without treatment, the impact on memory can become more severe, affecting various aspects of daily life and overall cognitive function. Recognizing and addressing these issues early can help mitigate long-term effects.
Strategies to Improve Memory in Depression
Managing memory problems associated with depression involves addressing both the mental health condition and its cognitive impacts. Here are some strategies that may help:
- Therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can help address negative thought patterns and improve cognitive function.
- Medication: Antidepressants can help balance brain chemistry, potentially improving both mood and memory function. Consult with a healthcare provider to find the right medication.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Regular physical exercise and a balanced diet can support overall brain health and cognitive function, helping to alleviate some memory issues.
- Mindfulness Practices: Techniques such as mindfulness meditation and stress management can reduce overall stress and improve memory function by calming the mind and enhancing focus.
In summary, depression can indeed affect memory, making it harder to recall and process information. Understanding the connection between depression and memory loss is crucial for managing both conditions effectively. Seeking professional help and adopting strategies to address both mental and cognitive health can improve memory and overall well-being.