In today’s world, many people use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to protect their privacy and access content that might be restricted in their region. But how do VPNs actually work, and why are they so popular?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts your internet traffic by routing it through secure servers, making your browsing activity private. This not only protects sensitive information, like passwords, from cybercriminals but also allows users to bypass geo-restrictions and browse anonymously.
However, there's much more to VPNs than simply connecting to a remote server. This guide will explore what VPNs are, how they work, and what to consider when choosing a VPN service.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN is a service that hides your Internet Protocol (IP) address, allowing you to browse anonymously. Breaking down the term, "virtual," "private," and "network" explains the concept:
- Virtual: VPNs are digital services, requiring no extra hardware to operate.
- Private: VPNs encrypt your connection, preventing others from monitoring your online activity.
- Network: They establish a secure connection between your device, the VPN server, and the internet.
A Brief History of VPNs
VPN technology originated from the need to secure online communication after the creation of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET), an early form of the internet developed by the U.S. Department of Defense. As the internet expanded, so did the risk of cyberattacks.
In the early 1990s, researchers developed early VPN protocols to secure online data transfers. Over time, the technology evolved, becoming more accessible to consumers in the mid-2010s as privacy concerns and the need for secure remote work increased.
Why Do People Use VPNs?
VPNs are widely used for various reasons:
- Privacy: Many users want to protect their online activity from being tracked by their Internet Service Provider (ISP) or advertisers.
- Security: VPNs provide an additional layer of protection when using unsecured networks, such as public Wi-Fi in coffee shops or airports.
- Access to Geo-Restricted Content: VPNs allow users to bypass regional restrictions, unlocking content not available in their location.
- Avoiding Censorship: VPNs can help users in regions with strict censorship to access blocked websites.
Is It Legal to Use a VPN?
Using a VPN is legal in most countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand. However, some countries, such as China, North Korea, and Russia, have made it illegal or heavily restricted. Even in places where VPNs are legal, using them to commit illegal activities remains prohibited.
Types of VPNs
Client-Based VPNs: These are the most common type of VPNs used by individuals. They work by installing software on your device that creates a secure connection to a VPN server.
SSL VPNs: Often used by organizations, SSL VPNs allow employees to securely access company networks remotely.
Site-to-Site VPNs: These are used to connect different networks, usually by large organizations with multiple locations that need to securely share data between sites.
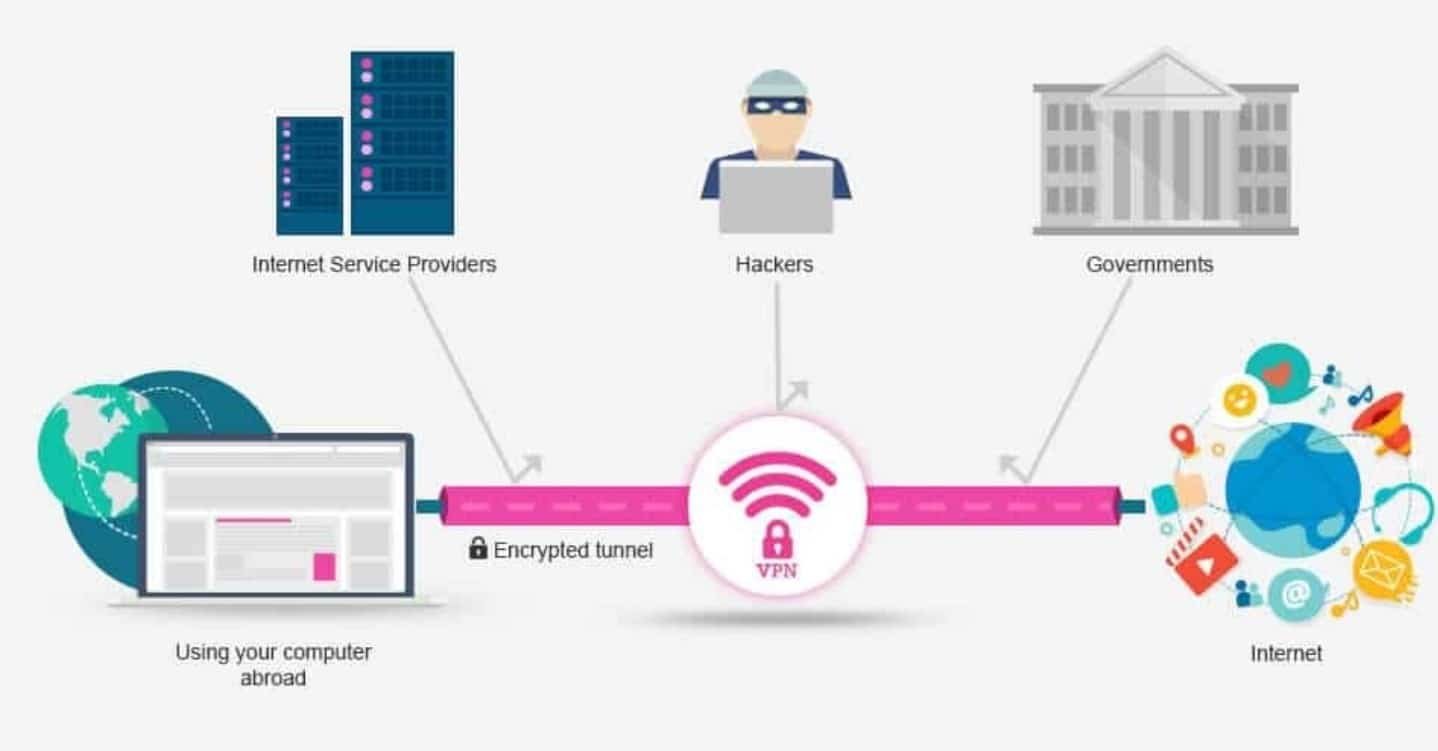
How Does a VPN Work?
When you connect to a VPN, it creates a secure tunnel between your device and the internet. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
Connect to the VPN Server: After turning on the VPN software, it connects your device to a VPN server that acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet.
Tunneling: Once connected, the VPN encrypts your data before sending it through the VPN tunnel. The VPN server retrieves data from the requested website, encrypts it, and sends it back through the tunnel.
Encryption and Decryption: The data is encrypted by the VPN server, sent to your device, and then decrypted by your VPN client, ensuring that your ISP and others cannot see what you’re doing online.
VPN Protocols
Different VPNs use various protocols to secure your data. Some common VPN protocols include:
- OpenVPN
- IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange Version 2)
- PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
- Wireguard
Each protocol offers varying levels of security and speed.
What Can a VPN Do?
VPNs offer several advantages, including:
- Concealing Your Internet Activity: VPNs prevent your ISP from tracking your browsing habits, offering privacy from advertisers and trackers.
- Blocking Malware and Trackers: VPNs protect you from cybercriminals who might attempt to intercept your data on unsecured networks.
- Encrypting Your Data: VPNs ensure that any information you send or receive online is encrypted, protecting your sensitive data from prying eyes.
Benefits of Using a VPN
Identity Theft Protection: VPNs help protect your personal information, such as banking details, from cybercriminals.
Preventing Price Discrimination: Some e-commerce sites adjust prices based on your location. VPNs help prevent this by masking your IP address.
Protecting Against DDoS Attacks: Gamers and streamers can use VPNs to protect themselves from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which disrupt their internet connection.
Working Safely From Home: VPNs allow remote workers to securely connect to their company’s network.
Accessing Geo-Restricted Content: VPNs make it possible to access content and websites that are restricted based on location.
How to Choose a VPN Service
With so many VPN providers available, selecting the right one can be overwhelming. Here are some tips for choosing the best VPN service for you:
List Your Options: Identify a few well-known providers, such as NordVPN, ExpressVPN, or SurfShark.
Evaluate Features: Look for essential features such as:
- A no-log policy to ensure your browsing activity is not tracked.
- An adblocker to block intrusive ads.
- A kill switch to protect your data in case your VPN connection drops.
- Multiple server locations to ensure fast and reliable connections.
Check Device Compatibility: Make sure the VPN works across all the devices you use, including computers, smartphones, and tablets.
Assess Server Locations: If you need to access content from a specific country, ensure the VPN has servers in that location.
Review Pricing: Compare pricing and look for money-back guarantees to ensure the service fits within your budget.
Final Thoughts
With 41% of U.S. adults using a VPN for work or personal use, it’s clear that VPNs have become essential tools for protecting online privacy and accessing content without restrictions. When choosing a VPN, make sure it offers robust security features, reliable server connections, and works across your devices.
What’s your favorite VPN? Do you have any recommendations or experiences to share? Let us know in the comments!




